Diseases
Hoba Therapeutics focuses on developing novel treatments for two large indications with clear unmet needs for novel, safe and efficacious medications.
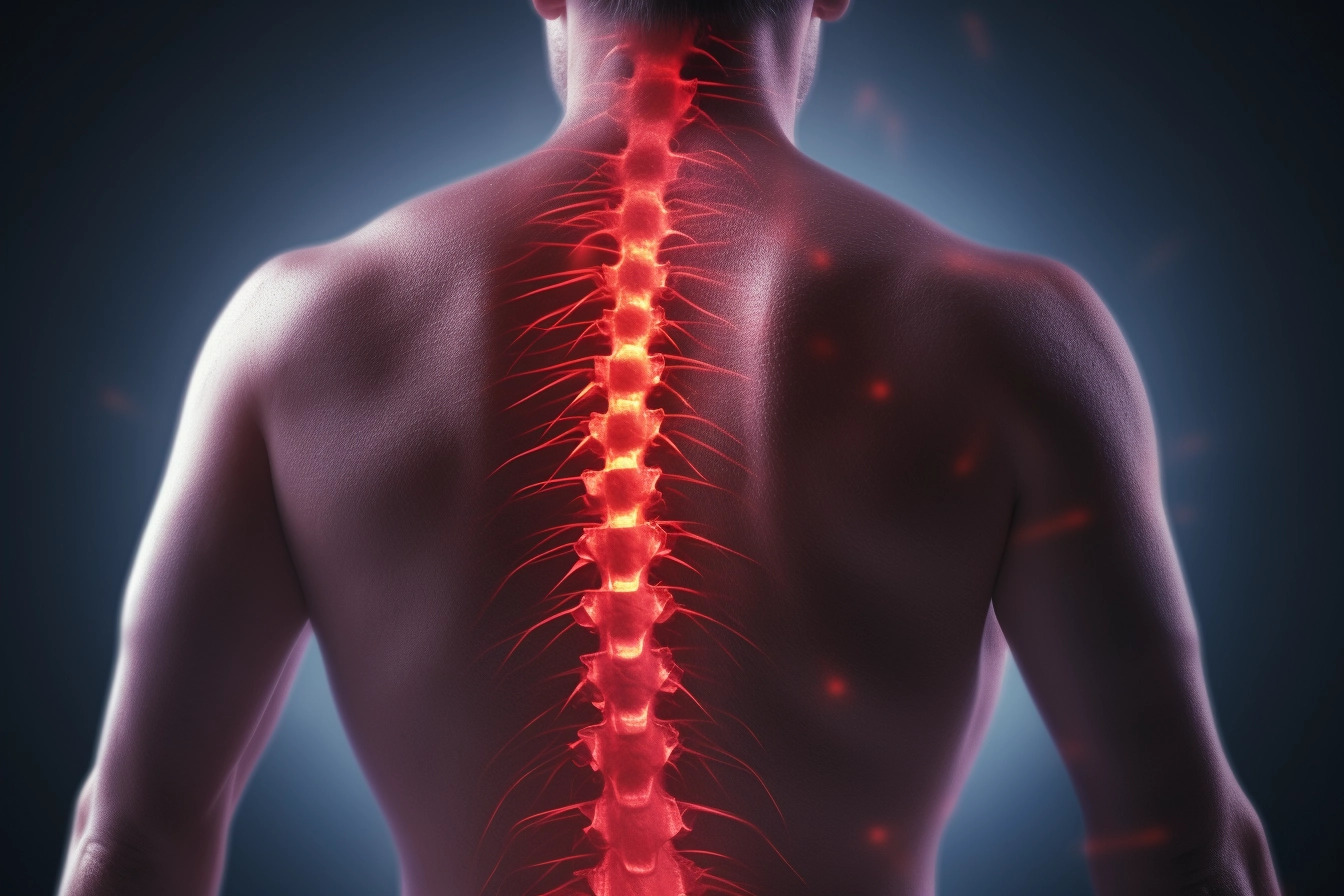
Neuropathic Pain
Chronic neuropathic pain is a significant global health issue, affecting a substantial portion of the population worldwide. In Europe, the prevalence is estimated to be 6–8% of the general population. Chronic neuropathic pain represents an enormous economic burden to society and a personal burden to the affected persons in the form of disability and loss of quality of life.
Neuropathic pain is a chronic disorder resulting from damage to or dysfunction of the nervous system. Causative factors are lesions in or disorders of the nervous system, such as injury, pressure, toxic agents (e.g., chemotherapy), viral infections, and metabolic disorders. These lesions lead to aberrant functioning of sensory nerve cells, resulting in a chronic, debilitating sensation of pain.
The complexity and variability of chronic neuropathic pain necessitate a multifaceted treatment approach and highlight the need for continued research and development of more effective and safer treatment options. The global neuropathic pain market is valued at USD 7.6 billion in 2023 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.2% during the next seven years.
Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain (CIPN)
CIPN is a painful and debilitating condition that occurs as a side effect of treatment with certain chemotherapy drugs used in cancer treatment. Chemotherapy drugs are powerful medications designed to kill or slow the growth of cancer cells, but they also affect healthy nerve cells in the peripheral nervous system, leading to peripheral neuropathy and pain.
Trigeminal neuralgia (TGN)
Trigeminal neuralgia, also known as tic douloureux, is a chronic pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, a cranial nerve responsible for transmitting sensory information from the face to the brain. This condition is characterized by sudden and severe facial pain that can be triggered by even mild stimulation of the trigger zones.
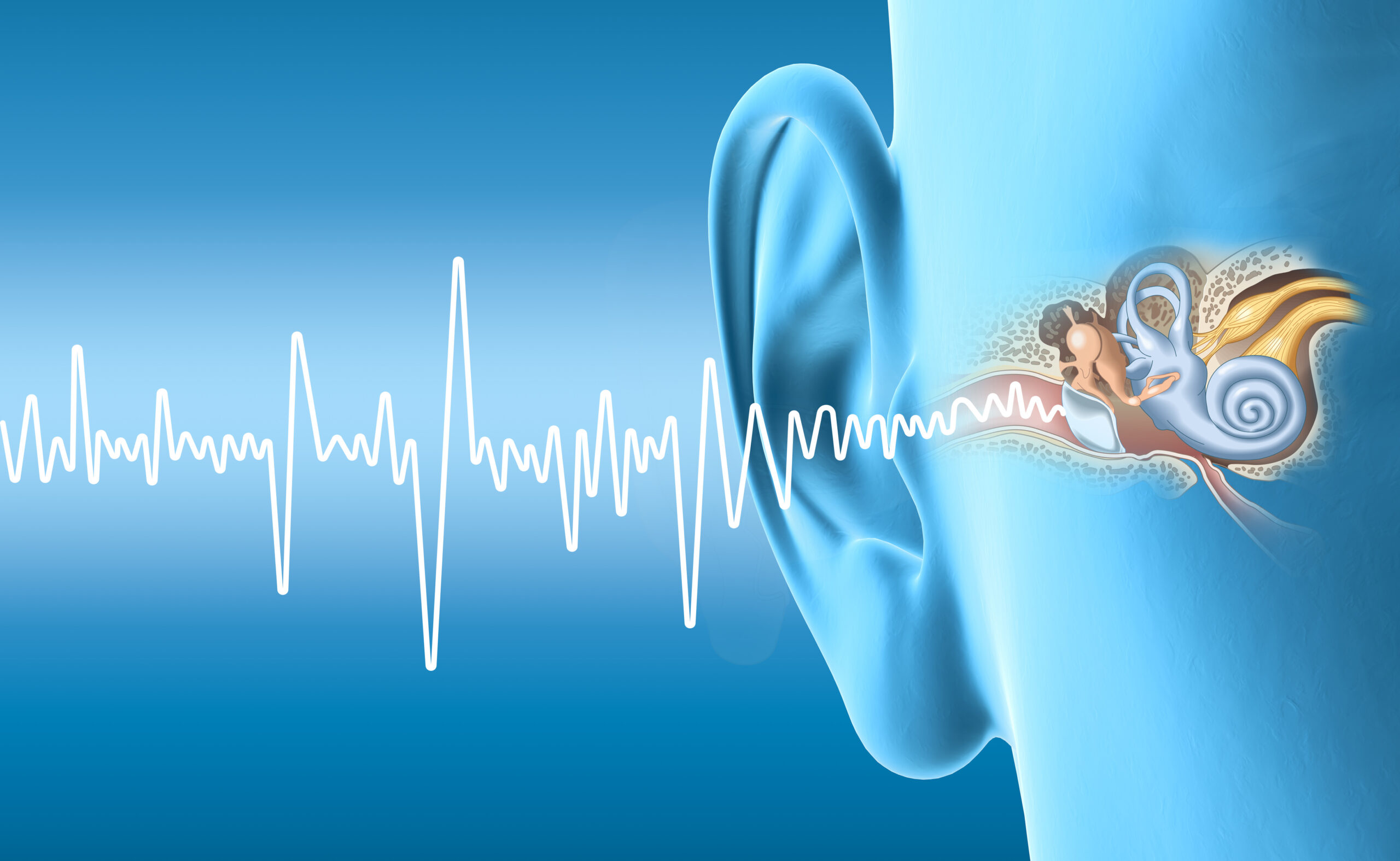
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is hearing loss caused by damage or dysfunction of the inner ear (cochlea) or the auditory nerve, which transmits sound signals from the inner ear to the brain. SNHL is highly prevalent and includes common types of hearing loss e.g. age-related-, noise-induced-, and toxic-induced- hearing loss.
SNHL is a common and significant health issue that affects a considerable portion of the population, particularly as people age. Current treatment options for sensorineural hearing loss are focused on hearing rehabilitation and include devices such as hearing aids and cochlear implants.
There is a clear clinical need for a pharmaceutical treatment of sensorineural hearing loss.
Ototoxic hearing loss (OHL)
Ototoxic hearing loss is caused by exposure to certain that have toxic effects on the structures of the inner ear mediating hearing (e.g. chemotherapy, aminoglycoside antibiotics). These substances, when introduced into the body, can damage the delicate hair cells in the cochlea and/or the auditory nerve, leading to hearing impairment or complete hearing loss.